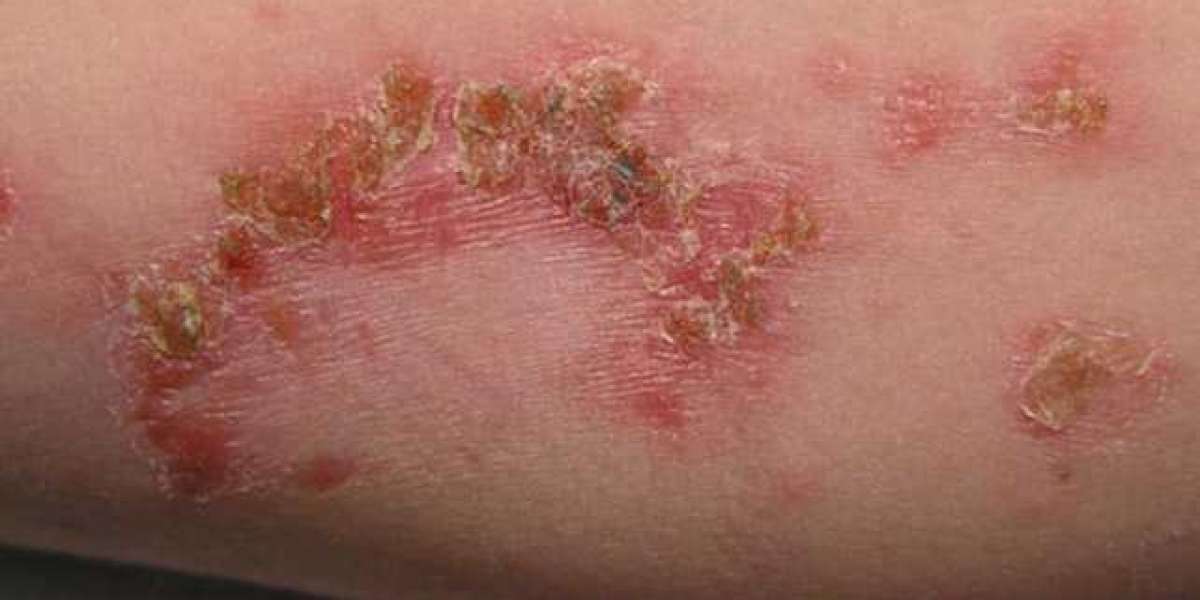
Causes of Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections are caused by the invasion of harmful bacteria into the body. These bacteria can enter through various means, such as:
- Direct Contact: Bacteria can spread through skin-to-skin contact, cuts, or wounds.
- Contaminated Food and Water: Ingesting bacteria from poorly cooked or contaminated food and water.
- Airborne Transmission: Breathing in bacteria from coughs, sneezes, or other respiratory secretions.
- Insect Bites: Some bacteria are transmitted through insect bites, such as those from ticks or mosquitoes.
- Environmental Exposure: Coming into contact with bacteria in soil, water, or surfaces that are contaminated.
Symptoms of Bacterial Infections
The symptoms of bacterial infections can vary widely depending on the type of bacteria and the area of the body affected. Common symptoms include:
- Fever: An increase in body temperature is often a primary sign of infection.
- Pain and Inflammation: Affected areas may become painful, swollen, and red.
- Fatigue: General feelings of tiredness and weakness.
- Pus or Discharge: In skin infections, pus or a yellowish discharge may be present.
- Difficulty Breathing: Respiratory infections may cause shortness of breath, coughing, or chest pain.
Diagnosis of Bacterial Infections
Diagnosing bacterial infections typically involves:
- Physical Examination: A doctor may check for signs of infection like swelling, redness, or abnormal sounds in the lungs.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests, urine tests, or cultures can help identify the type of bacteria causing the infection.
- Imaging Studies: X-rays, CT scans, or ultrasounds may be used to detect internal infections or complications.
Common Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections can occur in many different parts of the body. Some common types include:
- Respiratory Infections: Such as pneumonia or bronchitis, often caused by bacteria like Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Commonly caused by Escherichia coli, these infections affect the bladder, kidneys, and urinary tract.
- Skin Infections: Conditions like cellulitis or impetigo, which are often treated with Cephalexin 500Mg.
- Gastrointestinal Infections: Bacterial infections in the digestive tract can cause food poisoning, diarrhea, or other gastrointestinal symptoms.
Treatment of Bacterial Infections
Treatment usually involves antibiotics, which are prescribed based on the type of bacteria. Cephalexin 500Mg is a common antibiotic used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, particularly skin infections. The duration and dosage of antibiotic treatment depend on the severity of the infection and the patient's overall health.
Prevention of Bacterial Infections
Preventing bacterial infections involves several key practices:
- Hygiene: Regular handwashing and keeping wounds clean are essential.
- Vaccination: Immunizations can protect against certain bacterial infections.
- Safe Food Practices: Proper food handling, cooking, and storage can prevent foodborne bacterial infections.
- Avoiding Close Contact: Limiting exposure to infected individuals or contaminated environments.
Conclusion
Bacterial infections can range from mild to severe, but with proper diagnosis and treatment, including the use of Cephalexin 500Mg, most can be effectively managed. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments is crucial in reducing the risk and impact of bacterial infections.